Growth Hormone Peptides in 2026: The Complete Guide to Muscle Growth, Fat Loss & Recovery
The Future of Performance & Recovery: A Complete 2026 Guide to Growth Hormone Peptides
In today’s performance-driven world, athletes, fitness enthusiasts, biohackers, and longevity-focused individuals are constantly searching for smarter ways to optimize recovery, muscle growth, fat metabolism, and overall vitality. Among the most discussed innovations in this space are growth hormone peptides — compounds that support the body’s natural ability to produce and regulate growth hormone (GH).
As research continues to expand and protocols evolve, peptides are becoming a central topic in performance science. But with growing popularity comes confusion. What are growth hormone peptides? How do they work? Who are they for? And most importantly — how do you source quality products responsibly?
In this in-depth guide, we break down everything you need to know about growth hormone peptides in 2026.
What Are Growth Hormone Peptides?
Growth hormone peptides are short chains of amino acids designed to stimulate the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. Unlike synthetic growth hormone itself, these compounds work by signaling your body to increase its own natural production.
This distinction matters.
Instead of replacing a hormone, peptides support physiological pathways already present in the body. This makes them highly interesting in performance research and therapeutic investigations.
Some of the most widely discussed growth hormone-releasing peptides include:
-
GHRP family peptides
-
GHRH analogues
-
CJC variants
-
Ipamorelin
-
Hexarelin
How Growth Hormone Peptides Work
To understand peptides, we first need to understand growth hormone regulation.
Growth hormone secretion is controlled primarily by two hypothalamic hormones:
-
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) – Stimulates GH release
-
Somatostatin – Inhibits GH release
Growth hormone peptides generally fall into two categories:
1. GHRH Analogues
These mimic natural GHRH and signal the pituitary gland to increase GH output.
2. GHRP Compounds
These bind to ghrelin receptors and trigger GH release through a different pathway.
When combined strategically (as often explored in research settings), these pathways may work synergistically to produce amplified pulsatile GH secretion.
Why Growth Hormone Matters
Growth hormone plays a vital role in:
-
Muscle protein synthesis
-
Fat metabolism
-
Recovery from intense training
-
Collagen production
-
Bone density
-
Sleep regulation
-
Cellular repair
As we age, natural GH production declines significantly. By age 30, levels may begin to decrease steadily, and by 40–50, reductions become more noticeable.
This decline has led to increased interest in compounds that support natural GH stimulation.
Potential Research Applications of GH Peptides
It’s important to approach peptides from a research and performance optimization perspective rather than exaggerated marketing claims.
Here are some areas currently explored in research:
1. Muscle Growth & Strength Support
Growth hormone contributes to increased IGF-1 production, which plays a role in muscle development. Peptides that stimulate GH may support improved muscle recovery and hypertrophy when combined with structured training.
2. Fat Metabolism
GH is known to influence lipolysis — the breakdown of stored fat for energy. Research into GH-releasing peptides often examines their potential influence on body composition when paired with diet and resistance training.
3. Recovery & Injury Support
GH plays a role in tissue regeneration and collagen synthesis. This makes it an interesting compound in recovery research, especially for athletes experiencing repetitive strain or intense training cycles.
4. Sleep Optimization
Growth hormone secretion is closely linked to deep sleep phases. Some peptide protocols are studied in the context of sleep enhancement due to their impact on natural hormone pulses.
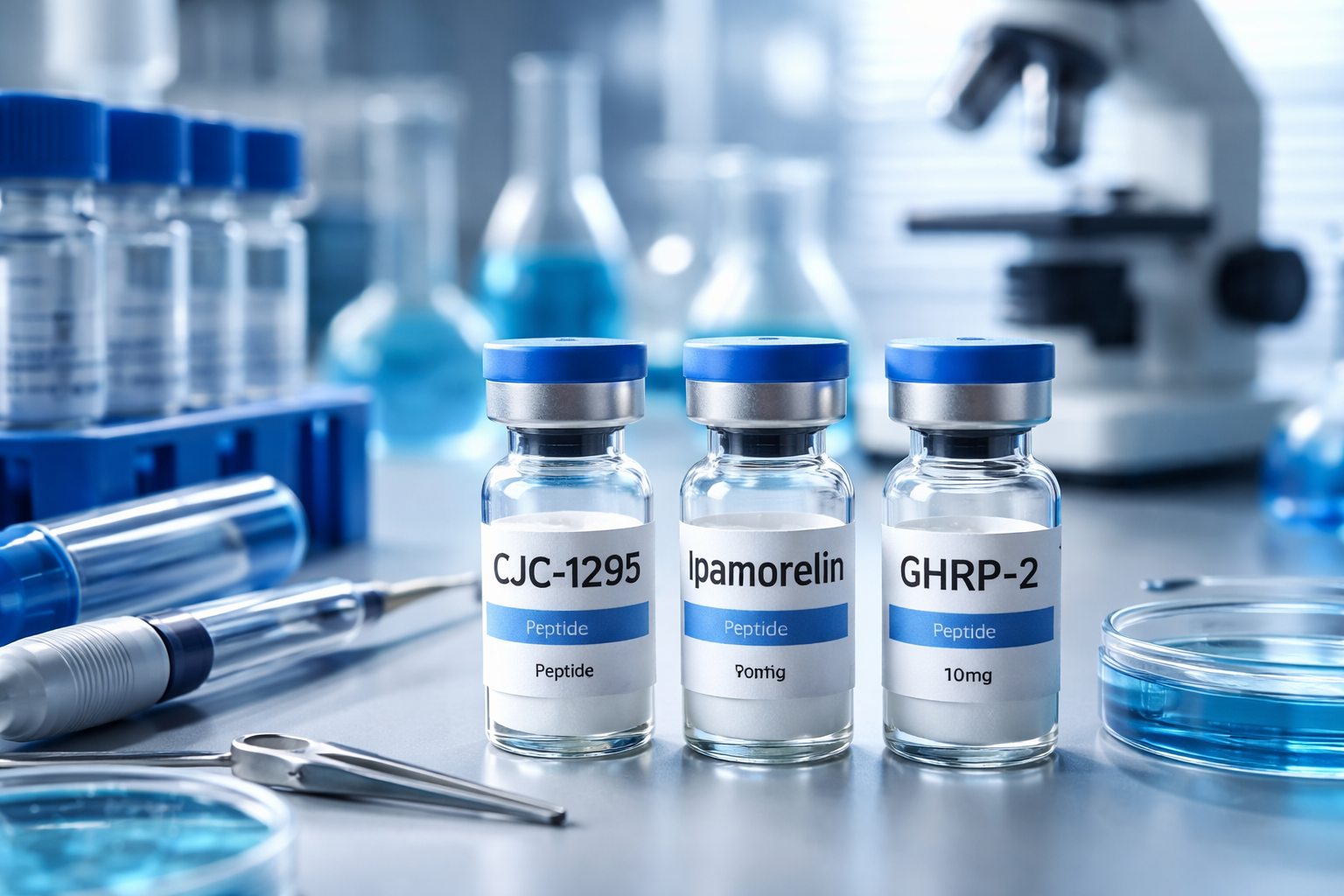
Popular Growth Hormone Peptides in 2026
Below are some of the most discussed peptides in performance communities:
CJC-1295 (With or Without DAC)
CJC-1295 is a long-acting GHRH analogue. The DAC (Drug Affinity Complex) version extends half-life significantly, allowing for less frequent administration in research models.
Ipamorelin
Known for its selective GH-stimulating properties, Ipamorelin is frequently studied due to its targeted mechanism and reduced interaction with cortisol and prolactin pathways.
GHRP-2 / GHRP-6
Earlier-generation GH-releasing peptides known for potent stimulation. These are widely studied but may produce increased hunger signaling.
Hexarelin
A powerful GH secretagogue studied for its strong pituitary stimulation effects.
Peptides vs Synthetic HGH: Key Differences
One major misconception is that peptides are the same as synthetic human growth hormone (HGH). They are not.
|
Peptides |
Synthetic HGH |
|---|---|
|
Stimulate natural GH production |
Directly introduce synthetic hormone |
|
Support natural hormonal rhythm |
Override natural secretion patterns |
|
Pulsatile release |
Continuous elevation |
This difference is why peptides are frequently preferred in research settings focused on physiological signaling rather than replacement therapy.
Quality Matters: Why Peptide Purity Is Critical
In the peptide industry, quality control is everything.
Because peptides are highly sensitive compounds, improper synthesis, contamination, or inaccurate dosing can drastically affect results.
When sourcing peptides, look for:
-
High purity percentages
-
Third-party testing
-
Proper storage protocols
-
Professional packaging
-
Transparent labeling
At Essentia Peptides, quality control remains a core principle of operation.
Understanding Peptide Cycles (Research Perspective)
In performance research, peptides are often studied in cycles rather than continuous long-term use. This is to observe:
-
Hormonal feedback patterns
-
IGF-1 response
-
Adaptation rates
-
Recovery response
Typical research cycles may range from 8–16 weeks, depending on the compound and research objective.
The Rise of Peptide Stacking
“Stacking” refers to combining two or more peptides to enhance complementary pathways.
Common research stacks include:
-
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin
-
GHRP + GHRH analogue
-
GH peptide + fat metabolism peptide
Stacking is explored to amplify natural GH pulses while maintaining physiological balance.
Peptides & Longevity Research
Beyond athletic performance, peptides are increasingly discussed in longevity communities.
Research areas include:
-
Cellular repair
-
Skin elasticity
-
Mitochondrial function
-
Age-related hormonal decline
As biohacking culture continues to grow globally, peptides are becoming central to discussions about aging optimization.
Legal & Regulatory Considerations
Peptide regulations vary by country and region. Many peptides are sold for research purposes only and are not approved for human consumption outside medical supervision.
It is essential for buyers to:
-
Understand local regulations
-
Purchase from reputable suppliers
-
Avoid exaggerated claims
-
Conduct proper research
How to Store Peptides Properly
Improper storage can degrade peptide structure and reduce effectiveness.
General storage guidelines include:
-
Keep lyophilized peptides refrigerated
-
Avoid light exposure
-
Store away from humidity
-
Use sterile handling practices
Why 2026 Is a Breakthrough Year for Peptides
The peptide industry has evolved significantly:
-
Increased demand globally
-
Higher manufacturing standards
-
Greater public awareness
-
Expanded research publications
What once existed only in niche bodybuilding forums is now discussed in medical, biohacking, and performance science communities.
Essentia Peptides remains committed to delivering products that align with modern quality expectations and professional standards.
Choosing the Right Peptide for Your Goals
When selecting peptides, research objectives matter.
Ask:
-
Is your focus muscle growth?
-
Fat reduction?
-
Recovery enhancement?
-
Hormonal optimization?
-
Sleep improvement?
Choosing the correct compound depends entirely on your intended research application.
Common Mistakes Buyers Make
-
Choosing based on price alone
-
Ignoring purity data
-
Buying from unverified suppliers
-
Following unstructured protocols
-
Not understanding hormone feedback loops
Avoiding these mistakes can dramatically improve research outcomes.
The Future of Peptide Science
Looking ahead, peptide science is expected to expand into:
-
Precision dosing
-
AI-assisted protocol design
-
Expanded therapeutic research
-
Advanced delivery systems
As regulatory landscapes evolve, quality-focused suppliers will dominate the industry.
Final Thoughts
Growth hormone peptides represent one of the most researched categories in modern performance science. From muscle development and fat metabolism to recovery and longevity exploration, these compounds continue to attract global attention.
However, quality sourcing, responsible research practices, and informed decision-making remain critical.
As 2026 unfolds, the peptide landscape is no longer experimental fringe science — it is structured, evolving, and increasingly refined.
If you’re exploring growth hormone peptides for research purposes, ensure you prioritize transparency, purity, and reliability.